『论文阅读』Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
/ / 点击 / 阅读耗时 3 分钟来源:Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Nets
源码:Github
这篇文章主要提供了一个基于cGAN的模型,并且利用这个general的模型可以同时应用到多个任务场景中去,而不需要额外设置模型结果和目标函数。
- Photos to semantic segmentation
- Cityscapes labels to photos
- Colorization
- Facades labels to photo
- Day to night
- The edges to photo
- And so on.
cGAN的generator: \[ G:{x, z} → G(x,z) → y \] x: input image, z: noise image, y: real image
Discriminator主要工作即尽量区分开\(G(x,z)\) 和\(y\) 的区别。而generator则尽量使得Discriminator区分不开。
本文的主要贡献是在cGAN的基础上做了一些改进。
Objective Function
对于目标函数进行了修改,在原有GAN网络的目标函数的的基础上,加上了L1约束,使得generator生成的图像与原图像尽量相近。感觉类似一个AutoEncoder的过程。
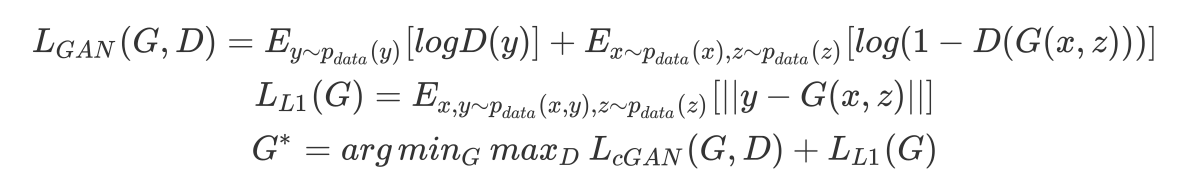
Network Architecture
Generator with Skips
A defining feature of image-to-image translation problems is that they map a high resolution input grid to a high resolu- tion output grid. In addition, for the problems we consider, the input and output differ in surface appearance, but both are renderings of the same underlying structure. Therefore, structure in the input is roughly aligned with structure in the output. We design the generator architecture around these considerations.
即认为原图和目标图片存在相同的底部结构。所以对于模型的生成部分,采用U-Net.
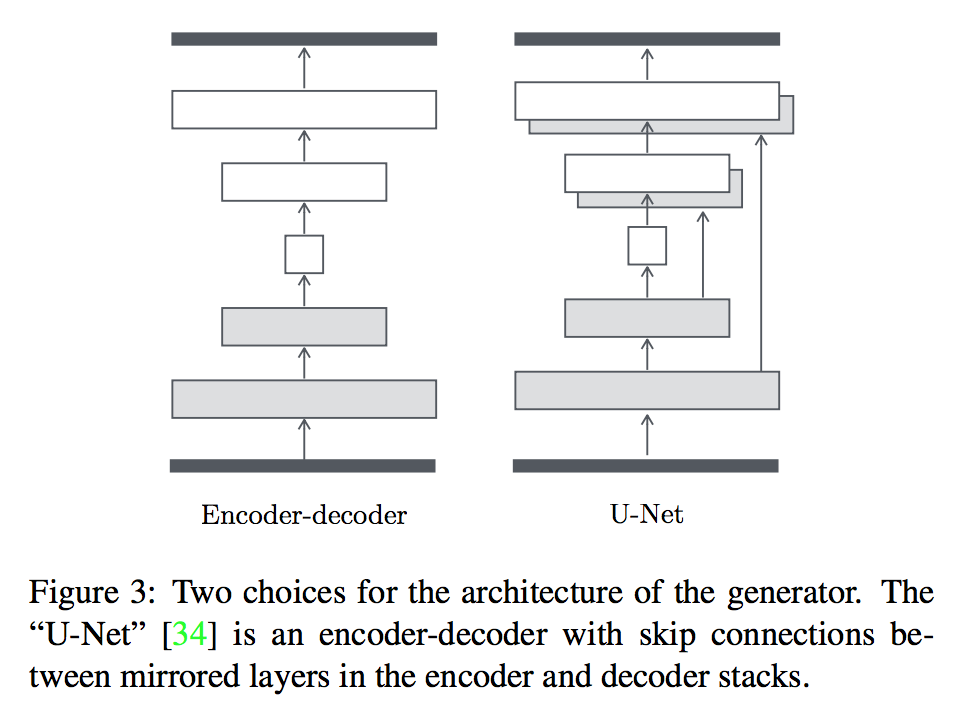
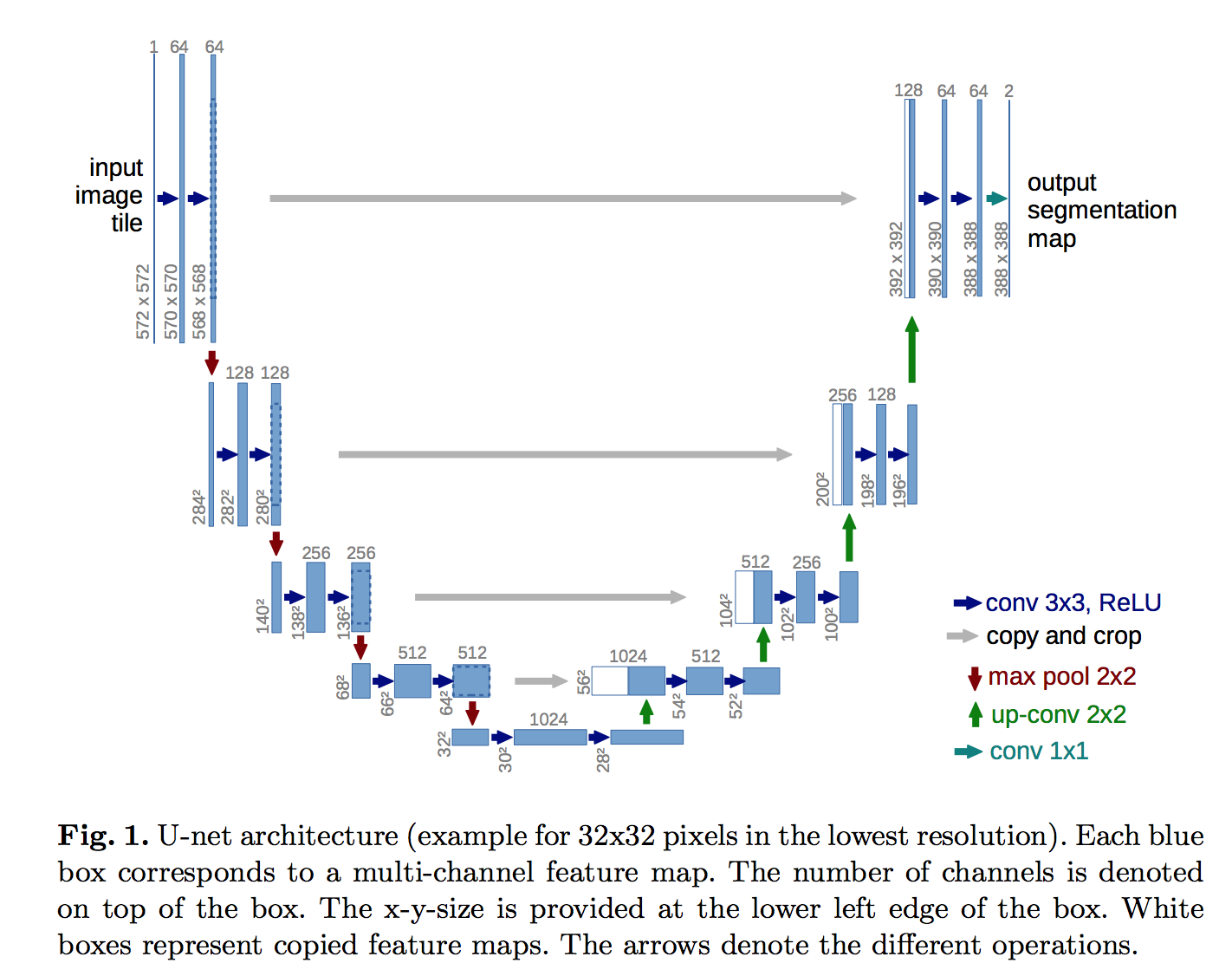
U-net 结构如下图:
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Markovian Discriminator
通常判断都是对生成样本整体进行判断,比如对一张图片来说,就是直接看整张照片是否真实。而且Image-to-Image Translation中很多评价是像素对像素的,所以在这里提出了分块判断的算法,在图像的每个\(N\times N\)块上去判断是否为真,最终平均给出结果。
总结:
The results in this paper suggest that conditional adver- sarial networks are a promising approach for many image- to-image translation tasks, especially those involving highly structured graphical outputs. These networks learn a loss adapted to the task and data at hand, which makes them ap- plicable in a wide variety of settings.